 2097
2097
 2018-06-19
2018-06-19
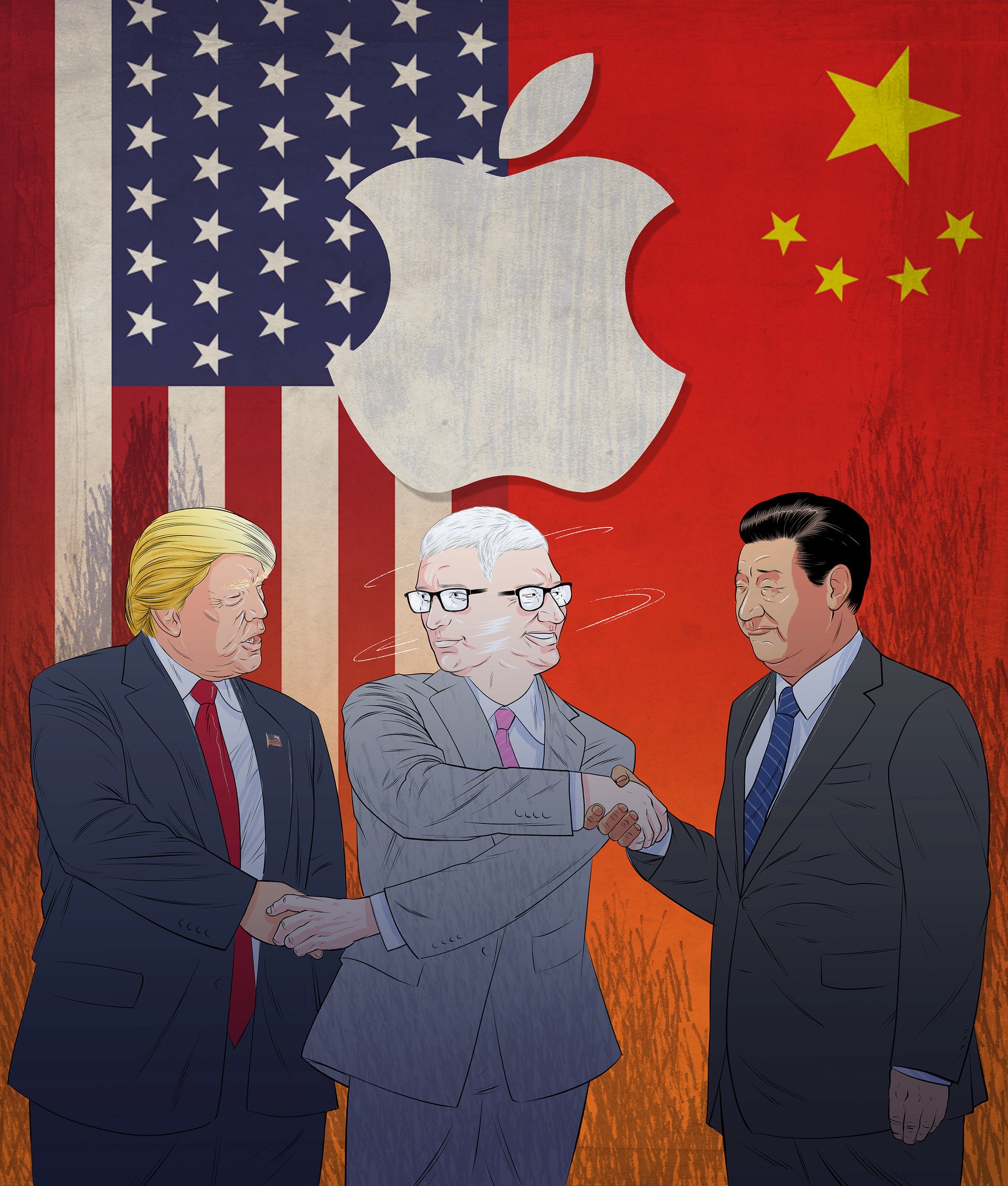
SAN FRANCISCO — Apple’s chief executive, Timothy D. Cook, may be the leader of the world’s most valuable public company, but lately he has had to act a lot like the tech industry’s top diplomat.
Last month he visited the Oval Office to warn President Trump that tough talk on China could threaten Apple’s position in the country. In March, at a major summit meeting in Beijing, he called for “calmer heads” to prevail between the world’s two most powerful countries.
In a trade and technology showdown between the United States and China, Apple and Mr. Cook have a lot to lose. With 41 stores and hundreds of millions of iPhones sold in the country, there is arguably no American company in China as successful, as high-profile and with as big a target on its back.

Since he took over Apple from its co-founder Steve Jobs, in 2011, questions about whether Mr. Cook, 57, could recreate the magic that led to the iPod and iPhone have persisted. For Mr. Cook, the analogous breakthrough — and potentially his legacy as the heir to Mr. Jobs — has come not from a gadget, but from a geography: China.
Under Mr. Cook’s leadership, Apple’s business in China grew from a fledgling success to an empire with annual revenues of around $50 billion — just a bit under a quarter of what the company takes in worldwide. He did this while China was tightening internet controls and shutting out other American tech giants.
Now, with the Trump administration saying on Monday that it will identify another $200 billion worth of Chinese goods that could face tariffs on top of the $50 billion already planned, and China having threatened retaliation, Apple is stuck in the middle.
The Trump administration has told Mr. Cook that it would not place tariffs on iPhones, which are assembled in China, according to a person familiar with the talks who declined to speak on the record for fear of upsetting negotiations. But Apple is worried China will retaliate in ways that hamstring its business, according to three people close to Apple who declined to be named because they were not authorized to speak publicly.
Apple fears “the Chinese-bureaucracy machine is going to kick in,” meaning the Chinese government could cause delays in its supply chain and increase scrutiny of its products under the guise of national-security concerns, according to one person close to the company. Apple has faced such retaliation before, another person said, and Reuters reported Ford vehicles are already facing delays at Chinese ports.
There is also concern that Apple could face reprisals for legal and regulatory efforts in Washington that have made it difficult for the Chinese tech giant Huawei to sell its phones and telecom equipment in the United States.
Apple executives and lobbyists in Beijing and Washington, led by Mr. Cook, have been trying to work both sides. They have fostered close ties to the administration of the country’s leader, Xi Jinping, an effort called Red Apple by employees at Apple’s manufacturing partner Foxconn, after the official color of the Chinese Communist Party.
Source: nytimes